Description
Here’s a comprehensive response to the prompt “exoskeleton architecture parameters”, incorporating images:
Key Architecture Parameters:
-
-
Actuation:
-
- Active: Powered by motors or actuators (e.g., electric, pneumatic, hydraulic) for force augmentation or rehabilitation.
-
- Passive: Stores and releases energy through springs, dampers, or elastic materials for support and load transfer.
-
- Hybrid: Combines active and passive elements for a balance of power and efficiency.
-
-
-
-
Kinematic Structure:
-
- Serial: Joints arranged in a linear chain, mimicking human limbs.
-
- Parallel: Joints connected to a common base, providing enhanced strength and stiffness.
-
-
-
-
Degrees of Freedom (DOF):
-
- Number of independent motions the exoskeleton can perform at each joint.
-
- Matches the DOF of the human body segment for natural movement.
-
-
-
-
Alignment:
-
- Anthropomorphic: Aligns with human joint axes for optimal force transfer and comfort.
-
- Non-anthropomorphic: May deviate from human anatomy for specific tasks or design considerations.
-
-
-
-
Joint Actuation:
-
- Direct drive: Actuators directly connected to joints, providing precise control but potentially bulky.
-
- Remote actuation: Actuators located remotely, using cables or Bowden cables for actuation, reducing weight and inertia.
-
-
-
-
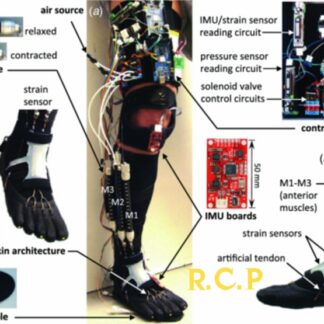
Sensors:
-
- Measure user movements, forces, and interactions for control and feedback.
-
- Include joint encoders, force sensors, IMUs (inertial measurement units), EMG (electromyography) sensors, etc.
-
-
-
-
Control Strategies:
-
- Impedance control: Adjusts exoskeleton stiffness and damping to assist or resist movements.
-
- Assist-as-needed: Provides assistance only when the user’s effort falls below a threshold.
-
- Adaptive control: Learns user preferences and adjusts behavior over time.
-
-
Additional Considerations:
-
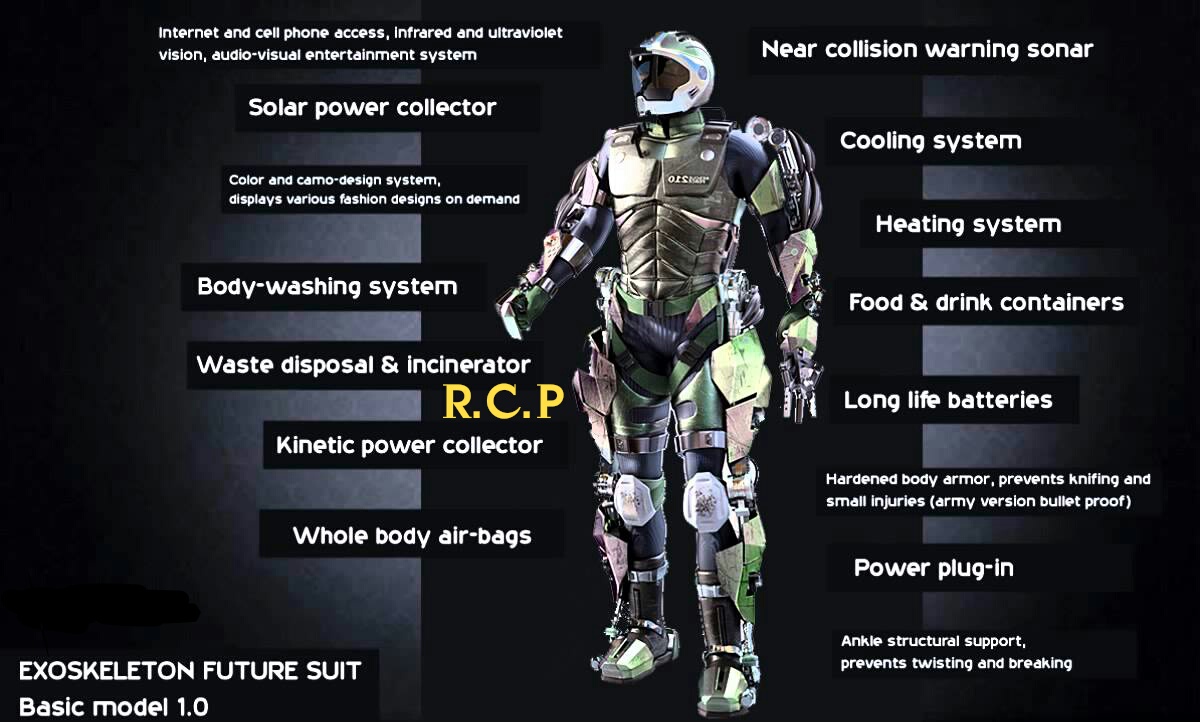
- Materials: Lightweight and durable materials (e.g., aluminum, carbon fiber, plastics) are essential.
-
- Power Supply: Battery life and management are crucial for active exoskeletons.
-
- Safety: Mechanisms for ensuring user safety and preventing injury are critical.
-
- Comfort: Proper fit and alignment are essential for user comfort and acceptance.
- Cost: Balancing performance and affordability is a key challenge in exoskeleton development.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.