Description
Exoskeletons work in a variety of ways, depending on their purpose and design. Here’s a breakdown of the two main types:
Passive exoskeletons:
-
-
These are the most common type and don’t have any motors or batteries. They rely on springs, levers, and linkages to transfer the weight and force of the user’s movements to different parts of the body, reducing strain on muscles and joints.
-
-
-
For example, a construction worker wearing a passive exoskeleton for the upper body might have the weight of their arms distributed across their core, making it easier to hold heavy tools overhead for extended periods.
-
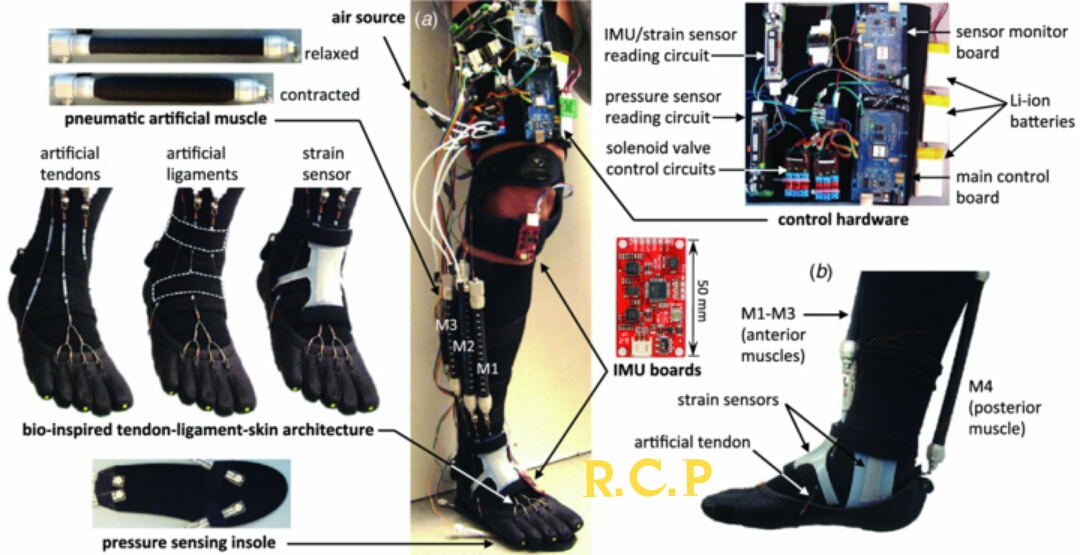
Powered exoskeletons:
-
-
These use electric motors and sensors to actively assist the user’s movements. Sensors detect the user’s muscle activity and send signals to the motors, which then provide additional force to amplify the user’s strength and range of motion.
-
-
-
Powered exoskeletons are more complex and expensive than passive ones, but they can offer greater assistance and enable users to perform tasks that would be impossible without them. For example, a person with spinal cord injury might be able to walk again using a powered exoskeleton.
-
Here are some additional details about how exoskeletons work:
-
- Frames: The frame of an exoskeleton is made of lightweight materials like aluminum or carbon fiber and is designed to fit snugly around the user’s body.
-
- Sensors: Sensors in powered exoskeletons detect muscle activity, joint angles, and other factors to determine how much assistance to provide.
-
- Actuators: Actuators, such as motors or hydraulics, are used to provide the additional force that amplifies the user’s movements.
-
- Power sources: Powered exoskeletons can be powered by batteries, or they can be tethered to a power source.
Exoskeletons are still in the early stages of development, but they have the potential to revolutionize many industries, from healthcare and rehabilitation to manufacturing and logistics. As the technology continues to improve, we can expect to see even more amazing applications for exoskeletons in the future.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.